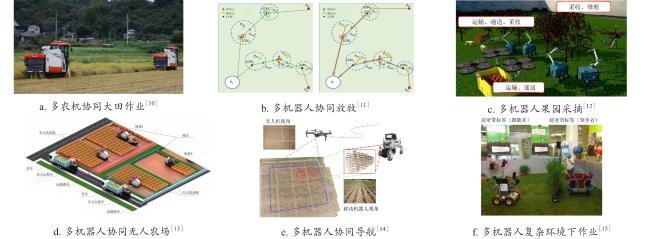
0 引 言
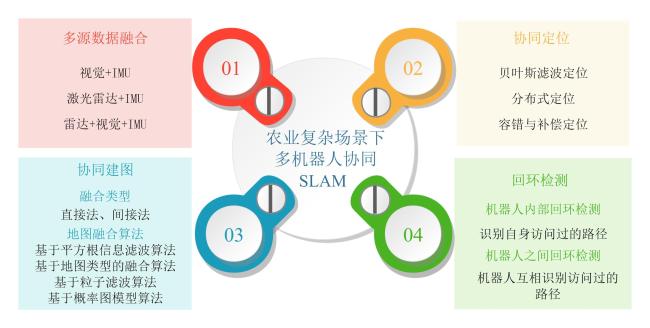
1 多机器人协同SLAM关键技术
1.1 传感器多源数据融合
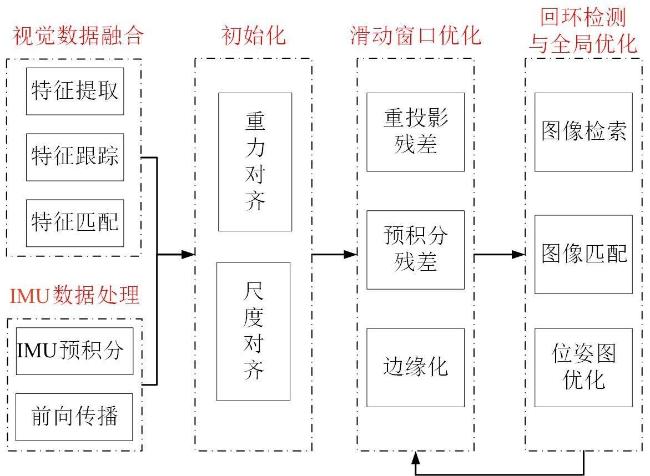
1.1.1 视觉+IMU
表1 VIO-SLAM代表性融合算法Table 1 Representative fusion algorithms of VIO-SLAM |
| 算法名称 | 硬件配置 | 融合类型 | 开源链接 | 年度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSCKF[32] | Mono+IMU | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/daniilidis-group/msckf_mono | 2007 |
| OKVIS[33] | Mono/Stereo+IMU | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/Ewenwan/okvis | 2013 |
| VINS-Fusion[34, 35] | Mono/Stereo+IMU | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/Ewenwan/VINS-Mono https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/VINS-Mobile | 2017 |
| ROVIO[36] | Mono+IMU | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/Ewenwan/rovio | 2017 |
| DM-VIO[37] | Mono+IMU | 松耦合 | https://cvg.cit.tum.de/research/vslam/dm-vio?redirect=1 | 2022 |
1.1.2 LiDAR+IMU
表2 LIO-SLAM代表性融合算法Table 2 Representative fusion algorithms of LIO-SLAM |
| 算法名称 | 硬件配置 | 融合类型 | 开源链接 | 年度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOAM[39] | LiDAR+Encoder | 松耦合 | https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/A-LOAM | 2014 |
| LeGo-LOAM[40] | LiDAR | 松耦合 | https://github.com/RobustFieldAutonomyLab/LeGO-LOAM | 2018 |
| LIO-Mapping[41] | LiDAR+IMU+GPS | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/hyye/lio-mapping | 2019 |
| LIO-SAM[42] | LiDAR+IMU | 紧耦合 | https://github.com/TixiaoShan/LIO-SAM | 2020 |
| Marked-LIEO[43] | LiDAR+IMU+Encoder | 松耦合 | / | 2022 |
|
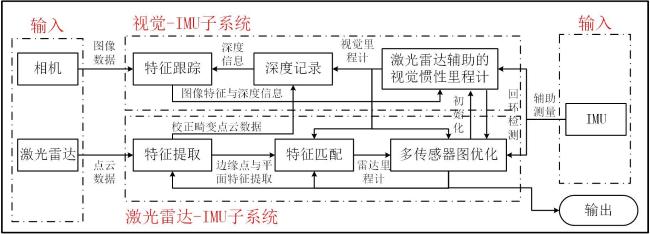
1.1.3 雷达+视觉+IMU
1.2 多机器人协同定位
表 4 多机器人协同定位主要算法Table 4 The main algorithms of multi-robot cooperative localization |
| 类别 | 应用场景 | 算法名称 | 策略优势 | 年度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝叶斯滤波定位 | 温室内环境监控机器人;养殖舍内畜牧监控机器人 | REHF[53] | 直接利用周围环境信息获取机器人之间的最优相对观测,具有异常干扰的动态环境中性能较好 | 2013 |
| STOC-EKF[54] | 采用计算传播雅可比矩阵提高估计的一致性和准确性 | 2015 | ||
| MP-KF[55] | 采用因子图模型、误差反向传播模型和基于误差反向传播算法来改善性能损失,在实际CL系统中具有实时性 | 2022 | ||
| Improved SHAEKF[56] | 引入了基于创新的卡方检验统计量来检测测量过程中的异常值,提高定位的准确性和可靠性 | 2022 | ||
| 分布式定位 | 果园采摘机器人;大田无人机喷洒农药 | Split-CIF[57] | 该方法的计算和通信复杂度与团队中的机器人数量成线性关系,在扩展到大规模的机器人团队时不会受到计算资源的限制 | 2014 |
| 分布式扩展卡尔曼滤波合作定位[58] | 通过机器人只存储自己最新的状态信息减少存储需求,不需要外部地标或已知位置的参考点进行定位 | 2018 | ||
| 分布式一致性扩展卡尔曼滤波合作定位[59] | 通过在转换后的坐标系统中执行状态估计,消除了由于不可观测维度减少导致的不一致性问题 | 2023 | ||
| BP-DCKF[60] | 基于无线传感器网络的节点定位,考虑了代理节点之间的合作,提高了定位精度,减少了参考节点的部署,节省了网络成本 | 2022 | ||
| 容错与补偿定位 | 天然草场下协同放牧机器人;批量无人农机协同大田作业 | FDEIF[61] | 在共享环境中定位一组相同的全向移动机器人,通过在分布式信息滤波框架内,采用模糊方法来提高定位的准确性和鲁棒性的挑战 | 2015 |
| DEKF[62] | 引入通信延迟到状态和测量方程,使用基于状态估计误差补偿的扩展卡尔曼滤波技术,在通信延迟的情况下提高定位的准确性 | 2019 | ||
| IPM[63] | 在动态环境下,通过使用IPM,允许机器人共享他们的传感器数据,根据所有机器人的最新和相关信息更新其定位来迅速适应这些变化 | 2019 | ||
| DCL-CU[64] | 每个机器人维护一个状态向量,只有当两个机器人相互测量时进行通信,能够有效处理异常传感器数据,支持通用测量模型 | 2021 |
1.3 多机器人协同建图
1.3.1 地图融合方法
表 5 基于不同融合类型的地图融合方法Table 5 Map fusion methods based on different fusion types |
| 融合类型 | 直接法 | 间接法 | 优势/局限 | 年度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 异构传感器进行地图融合[65] | 使用不同传感器数据构建独立网格地图 | 自适应蒙特卡洛定位算法重新定位一个机器人 | 能够整合异构传感器数据,对传感器数据的实时处理能力强; 依赖于精确的传感器数据、实验环境限制 | 2013 |
| 异构传感器进行3D地图融合[66] | 基于时间序列的地图合并框架直接进行融合 | 期望最大化迭代算法来估计机器人的相对变换 | 支持异构机器人和传感器配置,具有灵活性; 通信限制、依赖初始化 | 2014 |
| 稀疏地图与密集地图融合[67] | 地图匹配阶段通过期望最大化算法估计相对变换 | 通过时间序列的方式逐步合并地图 | 支持多种传感器,适应性和灵活性较强; 在处理大规模数据集时,期望最大化算法会增加计算负担 | 2019 |
| 不同机器人或不同时间点的地图融合[68] | / | 使用角点提取算法提取特征,构建同构方案,优化变换矩阵 | 无需姿态假设、高精度; 对角点的依赖、计算复杂度较高 | 2021 |
| 在未知环境中进行探索和地图融合[69] | / | 通过相似性函数对来自不同地图的特征点进行匹配,随机抽样一致性算法从匹配的特征点对中计算地图变换矩阵 | 地图实时合并效率高、减少重建时间; 通信依赖、数据类型限制 | 2020 |
| 在复杂环境中地图融合[70] | / | 构建基于角点的凸四边形和三角形来匹配重叠区域 | 适应性强、准确性提高、算法效率高; 角点依赖性、环境限制 | 2021 |
|
1.3.2 地图融合算法
表6 多机器人地图融合算法总结Table 6 Summarize of multi-robot map fusion algorithm |
| 分类 | 应用场景 | 算法 | 优势/局限 | 策略 | 时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于平方根信息滤波算法 | 未知环境下的野外机器人放牧 | C-SAM[71] | 无需初始对应关系、减少数据关联; 在处理大规模地图时计算复杂度较高 | 利用群体机器人信息共享的优化算法来合并不同机器人独立创建的地图,并且恢复每个机器人的完整轨迹 | 2008 |
| DDF-SAM 2.0[72] | 避免信息重复计数、一致性和鲁棒性较高; 通信要求较高、初始化和对齐问题 | 采用增强的局部系统,将局部地图和邻近机器人共享的信息融合成一致的地图 | 2013 | ||
| 基于地图类型的融合算法 | 无人农机自动导航 | MRTM-SLAM[73] | 局部度量地图的构建准确、可扩展性较强; 需要离线优化、计算资源要求高 | 构建固定大小的局部度量地图,通过添加边实现地图融合,边通过优化连接两个拓扑地图 | 2007 |
| MCS-SLAM[74] | 无需初始假设、地图融合转化为图像配准; 对角点提取的依赖、局部最优解 | 从网格地图中提取角点,计算初始最优变换矩阵,迭代优化变换矩阵,找到最大公共子图 | 2018 | ||
| R-map [75] | 减少了表示地图的数据量,提高处理效率; 局部地图之间的重叠区域较小时,算法的性能会减弱导致合并耗时较长 | 采用霍夫变换进行正交方向重对齐,网格地图转换为R-map,寻找共同特征合并局部地图 | 2020 | ||
| 基于上下文描述符的网格地图合并方法[76] | 多分辨率合并能力、上下文描述符; 分辨率差异敏感性 | 利用兴趣点的邻域信息建立初始匹配,估计两个网格地图之间的相似性变换。利用缩放修剪迭代最近点算法对初始变换进行细化,实现精确的网格地图合并 | 2021 | ||
| 无初始相对位置的多机器人栅格地图融合算法[77] | 无需初始位置信息、适应性强; 通信依赖、计算复杂 | 使用加速鲁棒特征检测技术提取多栅格地图的特征点,应用两步算法进行特征点匹配,利用随机样本一致性算法进行冗余特征的融合 | 2023 | ||
| 粒子滤波 | 养殖舍内动物行为监测;无人农场等 | Fast-SLAM[78] | 高效性、并行处理; 在未知数据关联下,地标的匹配会增加算法的复杂性 | 扩展了之前基于扩展卡尔曼滤波器的地图合并算法到Fast-SLAM算法。使用视觉传感器观察彼此和非唯一地标,并通过传播不确定性来合并地图 | 2010 |
| PLICP[79] | 提高准确性、迭代效率高; 重叠区域要求较高、噪声敏感性强 | 使用Fast-SLAM算法生成局部地图,然后通过机器人间观察计算初始对齐参数,最后使用PLICP算法更新这些参数 | 2012 | ||
| 分布式多机器人SLAM共识粒子滤波算法[80] | 提高地图构建质量、增强定位精度; 计算成本高、依赖有效通信 | 利用粒子滤波器来估计每个机器人的位置和地图,并通过共识算法在机器人之间传递和共享粒子权重,以达到全局一致性 | 2017 | ||
| WNCC[81] | 多传感器兼容性、协同定位能力强; 环境限制、计算资源需求高 | 由于全局和局部正射影像图的构建方法不同,导致地图质量和风格存在巨大差异,因此提出了WNCC算法来解决地图匹配问题。结合WNCC算法和粒子滤波器来实现实时定位 | 2020 | ||
| 修改后的快速SLAM方法[82] | 去中心化、考虑移动地标; 计算成本高、依赖有效通信 | 通过考虑环境中的移动地标来以去中心化的方式实现SLAM | 2023 | ||
| 基于概率图模型算法 | 大型果园的多机器人对果实的采收 | 高效因子图融合方法[83] | 内存优化、效率高、数值稳定; 应用范围小、实际部署困难 | 它重用各个因子图的变量排序来确定融合后图的排序。利用变量消除技术,优化变量的消除顺序来减少因子图求解过程中的计算复杂度和内存使用 | 2018 |
| 基于期望最大化的多机器人地图融合算法[67] | 通用性、高效性; 传感器限制、计算复杂 | 采用通用概率框架来解决集成地图融合问题,通过多数据关联地图匹配算法估计地图变换,借助时间序列地图合并算法,实现地图的逐步融合 | 2019 | ||
| MR-iSAM2[84] | 效率提升、信息流和全局优化; 算法复杂 | 该算法基于多根贝叶斯树,通过在不同的根分支中更新来自不同机器人的新测量数据,利用问题的稀疏性,提高了信息融合的效率 | 2021 |
1.4 回环检测
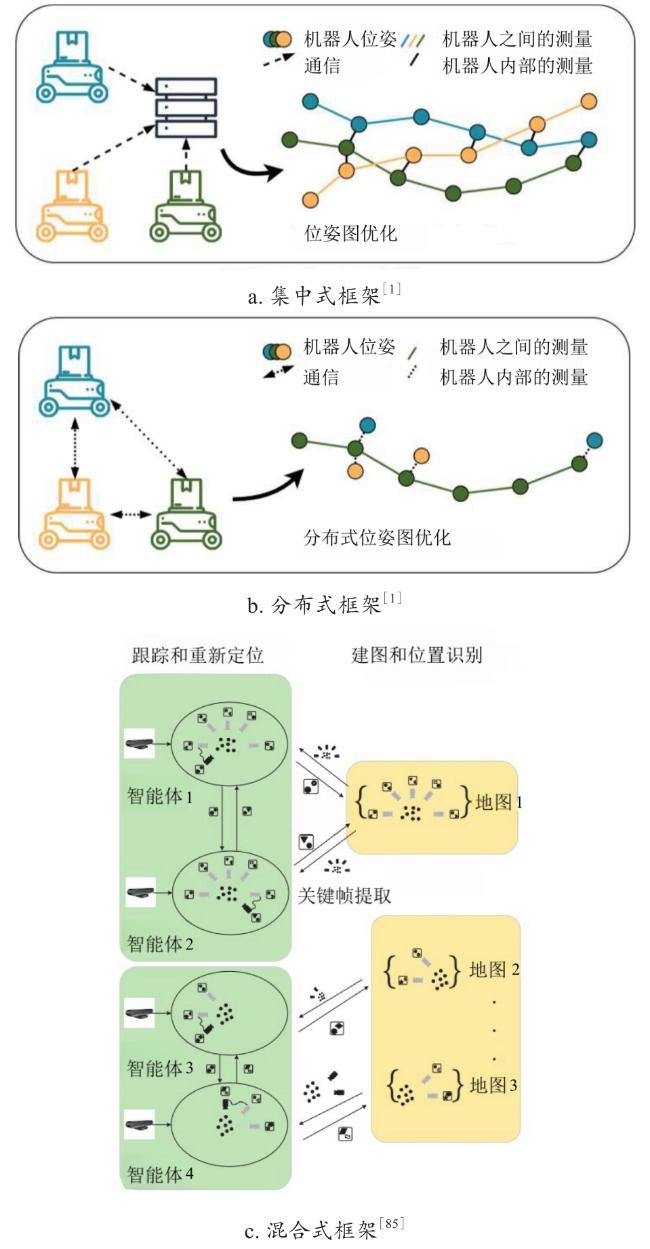
2 多机器人协同框架
表7 农业多机器人SLAM框架Table 7 Agricultural multi-robot SLAM framework |
| 框架名称 | 传感器 | 智能体 | 建图 | 协同方式 | 应用场景 | 地图类型 | 优化 | 优势 | 局限 | 代码链接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoSLAM[86] | C | UAV | Ce | 集中框架适用于大规模农田作业;精准农业监控;温室大棚管理 | GM | PGO Global BA | 采用坐标和参数联合编码与微小多层感知机作为场景表示,在合理的空洞填充和高效的内存使用下,实现建图和精确的跟踪 | 依赖于传感器的输入,对光照变化敏感 | https://github.com/HengyiWang/Co-SLAM | |
| CCM-SLAM[87] | C | UAV | S | Ce | GM | Global BA | 采用并行计算的方式,可以高效地处理大规模地图,并且保持较高的定位精度 | 凸优化和并行计算等技术,需要大量的计算资源 | https://github.com/VIS4ROB-lab/ccm_slam | |
| CVI-SLAM[88] | C,I | UAV | S | Ce | GM | Global BA | 可以实时处理计算机视觉和惯性传感器的数据,并实时更新定位和地图信息 | 在复杂环境或运动状态下,传感器的数据误差会导致SLAM精度下降 | / | |
| CVIDS[89] | C,I | UAV | De | Ce | GM | EM,LM,LCD | 无需深度传感器、实时性能强 | 计算资源需求高;针对光照变化强、纹理缺乏的区域会受到影响 | https://cslinzhang.github.io/CVIDS | |
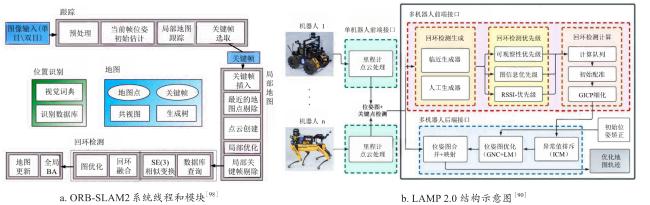
| LAMP 2.0[90] | L,I | UGV | De | Ce | GM | PGO,ICM GNC | 对不同里程计源和LiDAR配置的适应性强 | 在大规模机器人团队或通信受限的环境中性能较弱 | https://github.com/NeBula-Autonomy/LAMP | |
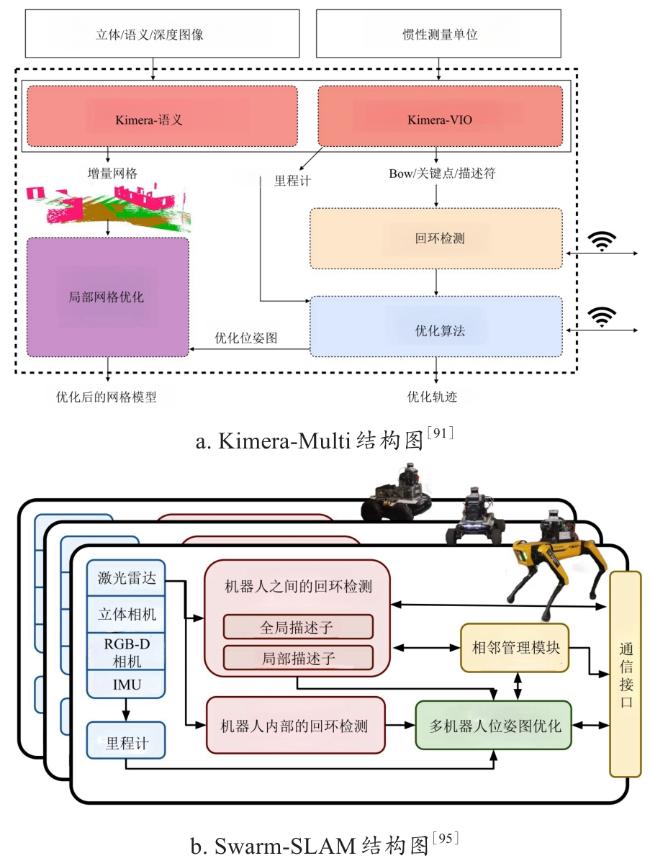
| Kimera-Multi[91] | C,I | UAV | De | D | 大规模牧场管理;远程或复杂地形作业以及协同除草和植保任务 | GM | Distributed PGO,GNC | 能够识别和拒绝由于感知别名造成的不正确的闭环闭合、减少了对中央服务器的依赖 | 通信延迟,带宽限制 | https://github.com/MIT-SPARK/Kimera |
| Door-SLAM[92] | C | UAV | S | D | GM | Distributed PGO,PCM | 不依赖外部定位系统、减少了对通信带宽的需求 | 面临同步问题和通信延迟 | https://github.com/MISTLab/DOOR-SLAM.git | |
| DiSCo-SLAM[93] | L | UGV | De | D | GM | two-stage PGO,PCM | 使用轻量级的Scan Context描述符,允许机器人之间交换观测数据,适用于带宽受限的通信环境 | 在处理大规模问题时两阶段优化方法可能需要较多的计算资源 | https://github.com/RobustFieldAutonomyLab/DiSCo-SLAM | |
| DCL-SLAM[94] | L | UGV | De | D | GM | PGO,RANSAC,PCM | 高精度、低带宽需求、前端传感器的灵活性 | 依赖点对点通信,中断或延迟影响系统的稳定性和性能 | https://github.com/PengYu-Team/DCL-SLAM | |
| Swarm-SLAM[95] | L,C | UGV | S | D | GM | GNC | 具有可扩展性、灵活性、分布式特性以及对有效的资源管理 | 内存限制和计算成本高 | https://github.com/MISTLab/Swarm-SLAM | |
| C2TAM[96] | C | UGV | S | H | 果园和葡萄园管理;多功能农场;应急响应和灾害管理 | LM | Local BA | 减轻了机器人平台的计算负担,同时还能利用云计算资源进行高效的地图优化和存储 | 依赖网络、云计算资源管理 | / |
| VOOM[97] | C | UGV | S | H | LM | Local BA | 结合高级对象和低级点作为分层标志物,提高定位精度、减少里程计漂移 | 对光照环境敏感 | https://github.com/yutongwangBIT/VOOM.git |
|
2.1 集中式
2.2 分布式
2.3 混合式
2.4 多机器人SLAM评价指标
表8 多机器人框架评价指标Table 8 Summary of the multi-robot framework |
| SLAM框架名称 | 数据集 | 评价指标 |
|---|---|---|
| CVI-SLAM[88] | EuRoC MAV Dataset (https://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets) | 准确性指标 (RMSE):0.050 m 比例误差(Scale Error):0.673% 效率指标(Processing Time):35.9 ms 鲁棒性指标(Loop Closure Detection):高 通信开销 (Multi-Robot SLAM):0.1~0.15 MB/s |
| Swarm-SLAM[95] | KITTI 00 (Stereo) (https://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/) | 准确性指标 (ATE):2.17 m 效率指标 (Processing Time):20.11 s 鲁棒性指标 (Map Merging):极高 通信开销:280 kB |
| S3E Square (LiDAR) (https://github.com/pengyu-team/s3e) | 准确性指标 (ATE):4.20 m 效率指标 (Processing Time):6.05 s 鲁棒性指标 (Loop Closure Detection):高 | |
| ORB-SLAM3[99] | EuRoC MAV Dataset (https://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets) | 准确性指标 (ATE):0.05~0.20 m 效率指标 (Processing Time):120~180 ms 鲁棒性指标 (Loop Closure Detection):极高 通信开销:中等偏高 |
| TUM RGB-D (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/tum-rgb-d) | 准确性指标 (RPE):0.02~0.08 m 效率指标 (Memory Usage):中 鲁棒性指标 (Dynamic Environment):中 | |
| RTAB-Map[100] | TUM RGB-D (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/tum-rgb-d) | 效率指标(Processing Time):100 ms以下 鲁棒性指标 (Handling Noisy Data):中 |
| EuRoC MAV Dataset (https://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets) | 效率指标(Computation Load):60~80 ms 鲁棒性指标 (Multi-Robot Fusion):高 |